The goal of Pilot Core A (PCA) for Alzheimer’s disease/Alzheimer’s disease related dementias (AD/ADRD) is to use a multidisciplinary, collaborative approach to identify, develop, refine, and disseminate promising technologies that have high potential to improve the health and wellbeing of older Americans living with AD/ADRD and/or their caregivers, with an emphasis on those that can mitigate current disparities in access and delivery of dementia care.
Core Leadership:
Core Activities:
- To develop an annual call and fund pilot studies focused on the application of AI and related technologies to improve the health and wellbeing of older adults with AD/ADRD and/or their caregivers
- To ensure pilot projects are well-designed, timely and rigorous by providing intellectual leadership, oversight, and access to all JHU AITC core resources
- To assist in the further development and translation of completed pilot projects into products that will benefit older adults with AD/ADRD and/or their caregivers
- To expand the expertise and network of funded investigators focused on advancing dementia- related AI technologies
Funded Projects
An AI algorithm to screen for and detect probable dementia cases in the emergency department.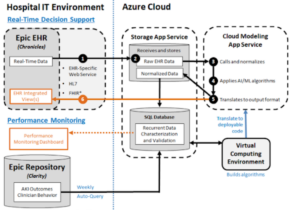
This project will produce a software product intended to aid in the detection of early MCI. Accomplishing these aims will assist clinicians on the front lines of early stages of dementia investigation, management, and treatment.

Wavi ECG Head Scanner
WellSaid.ai’s solution to address the need for early detection of cognitive impairment leverages simple to use, inexpensive in-home consumer technologies like the Amazon Alexa platform, equipped with scientifically validated, clinical grade cognitive assessments, modeled from gold standard assessment batteries. This solution allows screening, identification and clinical categorization of cognitive impairment and dementia well before an individual typically seeks medical attention and allows for large scale expansion of dementia screening and detection at an earlier and larger scale. WellSaid.ai’ A2 Pilot goal: Develop, test, and validate Machine Learning model(s) that accurately predict the cognitive status of older adults in their own home. The pilot has three objectives: 1) Retrospectively analyze our existing data sets to guide model development; 2) Prospectively collect comprehensive cognitive assessment data, including raw audio data from 160 patient-caregiver dyads from our in-home assessment technology; 3) Develop predictive models using Nature Language Processing and supervised learning algorithms that can identify and predict cognitive impairment prospectively.
People Power Company (doing business as Care Daily) will develop and research an AI Caregiver service called “Arti” that receives data from Apple Watches which enables it to send useful alerts, recommendations, and encouraging messages to caregivers watching over people with health problems such as Alzheimer’s Disease. “Arti” should be able to alert on falls, predict falls before they occur, detect wandering, and alert caregivers of the GPS location of a missing person with Alzheimer’s Disease, monitor sleep quality trends, offer recommendations for improving sleep quality, monitor fitness trends and recommend ways to improve caregiver health, and provide other senior care microservices.
The Sovrinti in-home system combines device utilization and real time location information to monitor seniors and their caregivers in home and assisted living environments. The rich sensor data allows continuous identification of ADLs and IADLs. For this project, Sovrinti would utilize AI techniques with de-identified data from an ongoing NIA Phase II study to preemptively identify adverse effects in seniors with cognitive challenges. This project utilizes the hundreds of months of available sensor data and the associated monthly health status reports to develop and validate the use of the Sovrinti system to predict rising risks of specific adverse events associated with senior care. These adverse events include urinary tract infections, covid events, falls, hospitalizations, etc. The approach combines an anomaly detection component with a trained embedding for each home or care recipient to create a risk prediction model. The risk prediction model would be used to establish alerts for caregiver intervention. In addition to the model development, the validation would establish confidence parameters for the alerts and quantify confidence level as a function of days prior to an adverse event with a goal of high confidence alerts occurring 2-5 days in advance of an adverse event.
This project will apply a deep-learning framework to develop a prediction model that can be commercialized as a service that offers personalized cognitive impairment risk prediction. Toward precision medicine and care, a deep-learning-based brain MRI analysis will be applied to provide an objective measure with which to quantify the risk for the development of cognitive impairment and identify modifiable factors that could accelerate or slow the pathological processes for each individual. This study will provide clues for disease prevention and therapeutic interventions.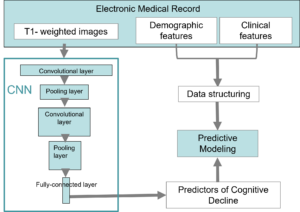
Sequoia is developing a wearable technology that makes AS accessible to older adults in the comfort of their own homes. By adapting this technology to the unique needs of older adults and packaging the complex sensors, circuitry, and algorithms required for AS into a comfortable and easy-to-use headband, we are translating this laboratory technique into an accessible therapy. This developmental work will entail an exploratory usability study to thoroughly understand essential design features. The resulting information will be used to focus our prototyping efforts as we continue our algorithm development. To validate the results of this work, we propose a small clinical feasibility evaluation of our prototype device.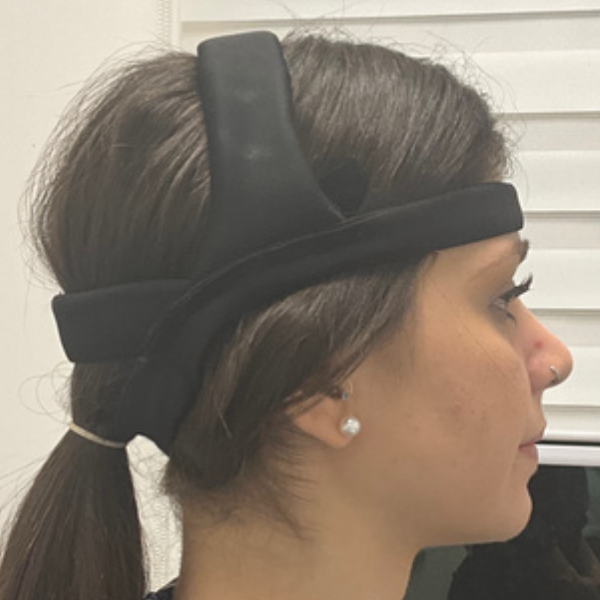
This is a mobile technology platform for home use that reports cognitive changes in an AD individual to their caregiver. The system will also provide a framework for quantifying cognitive fluctuations and lucid intervals in individuals with AD.
An AI-based facial expression analysis software will be integrated with an autonomous navigating robot which will visit nursing home residents who have advanced AD/ADRD to detect agitation. This can open opportunities to deliver nonpharmacologic interventions and to improve quality of care.
This project will apply AI analytics and electronic health records to develop/disseminate prediction models to identify persons with ADRD who would benefit from palliative care. The tools developed will support resource planning, quality and equity assessment within health delivery systems, health plans and communities.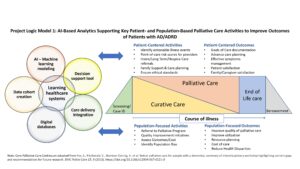
This is a virtual reality world for people with dementia that delivers therapies and activities of daily living engagement through an interface. The project will build with a AI-based dialog management system to make it more interactive and to allow caregivers more down time.
To advance the use of digital technologies in diagnosing early stages of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and mild cognitive impairment (MCI), we propose a research project using voice recordings, neuropsychological tests, neuroimaging, and neuropathology data. By developing interpretable deep learning models, we aim to identify cognitive abnormalities in speech that align with brain atrophy patterns and neuropathology grades. The project’s success will provide a validation framework for researchers and expand the application of voice technologies, making them accessible to diverse populations.
EZ-Aware is an easily accessible digital health platform that uses active and passive monitoring of cognitive and behavioral functions in older adults’ everyday environments. Current cognitive screening tools to detect Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) are time-consuming, are not used routinely, do not assess functional abilities in daily life, and are not sensitive to the earliest signs of neurodegenerative disease. To overcome these current barriers and limitations of cognitive screening in older adults, the goal of the A2Pilot project is to design a functional version of EZ-Aware that will be piloted for feasibility among cognitively healthy individuals and those with MCI. All the study data will be used to form a digital twin model, a digital representation of each individual participant in the study.

Emerging data suggest COVID-19 increases the risk for or potentiates the onset of Alzheimer’s disease in older adults. Those living in underserved urban as well as rural communities face distinct challenges in accessing dementia care. There is an urgent need to identify novel methods to evaluate the impact of COVID-19 on the cognitive health and dementia risk of older at-risk adults, and to do so in a manner that facilitates access for those in low resource settings. The DANATM Cognitive Assessment Tool is an FDA-cleared mobile application developed and validated to detect subtle cognitive dysfunction. The study team has successfully partnered with DANA developers to track cognitive trajectories following COVID-19. In this prospective cohort study, older adults will complete the DANA battery on multiple occasions following COVID-19 illness. By applying machine learning techniques to the in-home, app-based measurement of cognition this project will develop a more accurate, reliable, and accessible method of detecting and predicting cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s risk following a COVID-19 illness.
The EyeControl platform is designed to support communication with patients in the ICU, to improve communication (between patients, families, and the medical team) and aims to support the management of delirium. This project will evaluate the efficacy of the EyeControl platform specifically in older adults admitted to the ICU at JHU, and pilot new device features for delirium management via the device.
This project will develop methods for accurate and non-intrusive assessment of NPS at home over time, document the sequence of occurrences of NPS, predict adverse events, and provide interpretable data for accurate diagnosis. We will develop a clinician dashboard summarizing patients’ trajectories of NPS-related behaviors and correlate these measures with the onset of dementia. The goal of this project is to build the infrastructure for a largescale clinical trial.



